Calculate Discretionary Income – A Comprehensive Guide for You
The concept of discretionary income is crucial in personal finance management, as it indicates the funds remaining after essential expenses like housing, food, and taxes have been paid. This income differs from disposable income, which is used for necessities, as discretionary income can be spent on non- essential activities such as entertainment, travel, or savings. Understanding how to calculate your discretionary income can aid in developing a financial plan that balances saving and enjoying life. This article explains the steps to calculate it and its role in effective budgeting.
What is Discretionary Income?
Discretionary income is the money remaining after all necessary expenses, such as rent, utility bills, taxes, and essential groceries, have been paid. This portion of income can be used at one’s discretion for non-essential purchases or savings and investments. While often confused with disposable income, discretionary income is specifically allocated for non-essential spending. Understanding this distinction helps individuals manage their finances better, ensuring funds are distributed wisely and preventing overspending on non- essential items.
- Budget Allocation : Clearly distinguishing discretionary income aids in precise budget allocation.
- Spending Priorities : Identifying discretionary income helps prioritize spending on desired items.
Step 1 - Calculating Your Gross Income
To begin calculating your discretionary income, you must first understand your gross earnings. This is the total income before taxes or deductions, including wages, salaries, bonuses, or other earnings like freelance work and rental income. Recognizing your gross income is crucial as all subsequent deductions come from this initial amount. Accurately reporting your total income ensures your calculations reflect your actual financial status, laying a solid foundation for effective budget planning.
- Income Sources : Include all possible income sources to get an accurate gross income figure.
- Regular Updates : Regularly update your gross income to account for any changes in earnings.
Step 2 - Determining Essential Expenses
Essential expenses are the mandatory costs you regularly incur, and these need to be considered when calculating your discretionary income. These expenses include rent or mortgage payments, groceries, utility bills, health insurance, transportation, and debt repayments. Summing up these compulsory costs gives a clearer view of the money needed to maintain a stable lifestyle. Subtracting your essential costs from your total income provides your disposable income, which is the first part of determining available funds for discretionary spending. Accurately listing these expenses is crucial to avoid errors when determining cash available for non-essential purchases.
- Expense Categorization : Properly categorize expenses to ensure all essentials are included.
- Expense Tracking : Maintain records of essential expenses to facilitate accurate calculations.
Step 3 - Understanding Disposable Income
Disposable income is the amount of money left after all federal, state, and local taxes have been deducted from your total income. This specific amount represents the remaining resources to cover essential costs like food and housing. However, it doesn’t yet account for discretionary spending. By subtracting indispensable expenses from this disposable income, we can see the funds available for optional purchases. Understanding your disposable income helps prioritize essential expenses and provides a budget for discretionary expenditures without affecting basic needs.
- Tax Considerations : Ensure all applicable taxes are accounted for when calculating disposable income.
- Income Verification : Verify your disposable income periodically to reflect any changes in tax obligations.
Step 4 - Calculating Your Discretionary Income
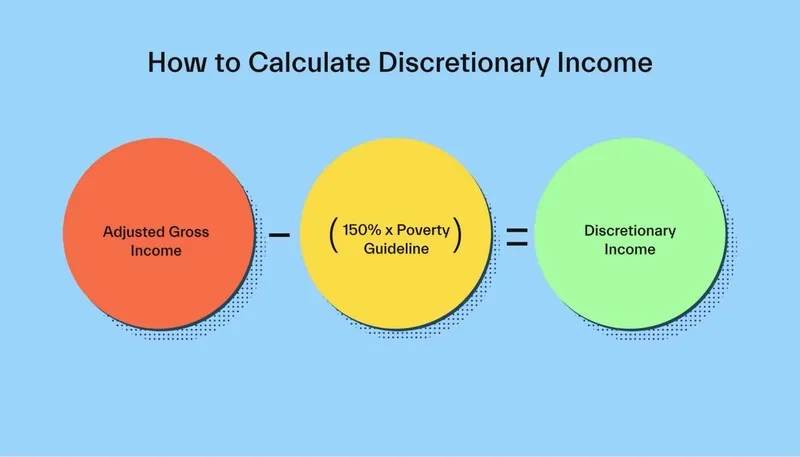
To calculate your discretionary income, start with your disposable income and subtract all necessary living expenses. The remaining amount is your discretionary income, which can be used for non-essential purchases, savings, or investments. For example, if you have a monthly disposable income of $4,000 and essential expenses total $2,500, your discretionary income is $1,500. This figure reflects the money you can allocate to lifestyle choices or savings growth. Properly calculating this amount helps set realistic financial goals and manage spending efficiently.
- Regular Reviews : Recalculate your discretionary income regularly to adapt to financial changes.
- Goal Setting : Use discretionary income to set and achieve specific financial goals.
Budgeting Using Discretionary Income
Effectively budgeting your discretionary income can lead to more balanced financial management that incorporates necessary expenses, desired lifestyle, and savings goals. To make the most of this additional income, consider dividing it between immediate desires and future savings. You might allocate part of this income for enjoyment or hobbies while reserving other portions for unexpected expenses or future investments. By planning discretionary spending carefully, you can avoid financial stress and build a more secure financial foundation. This thoughtful approach ensures present enjoyment and future stability.
- Priority Allocation : Prioritize discretionary spending to align with your financial objectives.
- Flexible Budgeting : Allow flexibility in your budget to accommodate unexpected opportunities or needs.
Tips for Managing Discretionary Income Wisely
Managing discretionary income requires careful monitoring of spending and prioritizing financial goals. To avoid unnecessary expenditures, review your budget regularly to ensure funds are directed towards meaningful purposes. Setting limits for leisure expenses, such as dining out or hobbies, can help maintain a balanced budget. Allocating a portion of your discretionary income for savings or investments can improve financial well-being and provide a cushion for unforeseen costs. By monitoring discretionary spending, you can enjoy your income while maintaining focus on long-term financial goals, achieving both stability and fulfillment.
- Spending Limits : Establish clear spending limits to prevent overspending on non-essentials.
- Financial Tracking : Use financial tracking tools to monitor and adjust discretionary spending as needed.
Conclusion
Understanding discretionary income and its role in financial planning can significantly impact your financial well-being. By calculating it thoughtfully and distributing it wisely, you can meet essential needs while having flexibility for non-essential spending. Whether your goal is saving, investing, or spending, a clear understanding of your discretionary income provides a strong foundation for making informed financial decisions that support both immediate pleasures and future security.