How to Lower Your Resting Heart Rate
Enhancing your cardiovascular health and overall fitness is a great way to monitor improvements in your resting heart rate. A lower resting heart rate often indicates good heart function, low stress levels, and overall physical fitness. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover practical ways to lower your resting heart rate by implementing lifestyle changes, exercise routines, and relaxation techniques.
Understanding Resting Heart Rate: What is it and Why Does it Matter?
 Your resting heart
rate is a key indicator of your general health and fitness. But what exactly
is it, and why does it matter? Let’s take a closer look.
Your resting heart
rate is a key indicator of your general health and fitness. But what exactly
is it, and why does it matter? Let’s take a closer look.
Resting Heart Rate Defined
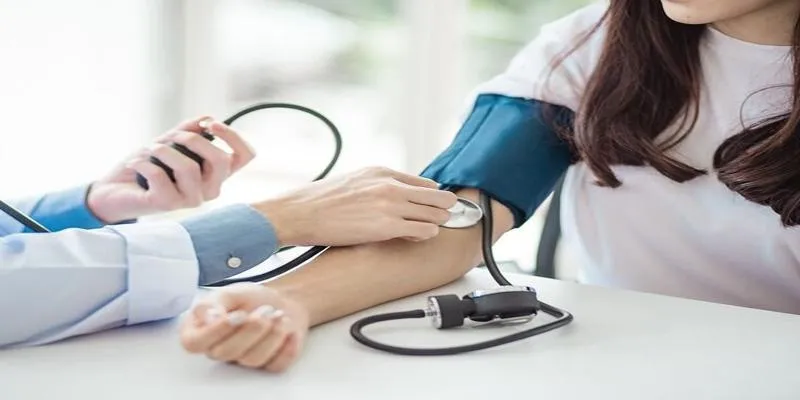
Resting heart rate (RHR) is the number of times your heart beats per minute when you are completely at rest. It’s usually measured in the morning before getting out of bed. For adults, a normal resting heart rate ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute, though athletes and very fit individuals may have an RHR as low as 40.
What Your RHR Means
Your resting heart rate is more than just a number; it’s a window into your cardiovascular health. Generally, a lower RHR indicates higher fitness levels and more efficient heart functioning. Here’s why it matters:
- Cardiovascular Health: A lower RHR is associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular diseases and indicates a healthy heart.
- Level of Fitness: As your heart becomes more efficient through improved cardiovascular fitness, your resting heart rate tends to decrease.
- Stress Levels: A high RHR can be a sign of chronic stress or anxiety.
- Recovery and Overtraining: Athletes use RHR to monitor recovery and prevent overtraining. An elevated RHR may indicate the need for more rest.
Factors Affecting Your Resting Heart Rate
 Your resting heart
rate is influenced by various factors, some within your control and others
not. Understanding these factors can help you work towards optimal
cardiovascular health.
Your resting heart
rate is influenced by various factors, some within your control and others
not. Understanding these factors can help you work towards optimal
cardiovascular health.
Age and Genetics
As you age, your resting heart rate typically increases. Aging causes changes in your heart’s anatomy and physiology. Genetics also plays a role, as some individuals naturally have higher or lower resting heart rates.
Physical Fitness and Activity Level
Regular exercise, especially aerobic activities, can lower your resting heart rate. As your heart becomes stronger and more efficient, it can pump more blood with each beat, reducing the need for frequent beats to circulate blood throughout your body.
Stress and Emotional State
Mental and emotional conditions directly impact your heart rate. Long-term stress, anxiety, and emotional issues can elevate your resting heart rate. Conversely, relaxation techniques and good mental health can help maintain a normal heart rate.
Lifestyle Factors
Several daily activities affect your resting heart rate:
- Diet: A healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can positively influence heart rate.
- Hydration: Proper hydration maintains blood volume, enhancing heart efficiency.
- Sleep: Adequate, quality sleep is crucial for heart health and can help lower resting heart rate.
- Substance Use: Caffeine and nicotine can raise your resting heart rate.
Proven Ways to Lower Your Resting Heart Rate
Your overall cardiovascular health and fitness benefit from the following strategies to lower your heart rate:
Regular Aerobic Exercise
Engaging in regular cardiovascular exercises is one of the most effective ways to lower your resting heart rate. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate- intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling can enhance heart efficiency, gradually slowing your resting heart rate.
Practice Relaxation Techniques
Chronic stress can increase your heart rate, so incorporating relaxation into your daily routine is essential. Try deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to activate your body’s relaxation response. These practices can lower your heart rate in the moment and contribute to a reduced resting heart rate over time.
Eat a Healthy Diet
Your diet significantly impacts heart health. Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, processed foods, and excess salt. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for the heart. Proper hydration is also critical, as dehydration forces your heart to work harder, increasing your heart rate.
Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for a healthy heart rate. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night, maintaining a consistent schedule and bedtime routine to improve sleep quality. Poor sleep can elevate stress hormones, which may increase your resting heart rate.
Tracking Your Progress: Measuring and Monitoring Your Resting Heart Rate
Monitoring your resting heart rate is essential to understanding your cardiovascular health and evaluating the effectiveness of your efforts to lower it. Here’s how to measure and track your progress effectively:
Manual Measurement Techniques
The simplest way to measure your resting pulse is by using your fingers on a pulse point. Place your index and middle fingers on the inside of your wrist or the side of your neck. Count how many times your heart beats in 30 seconds and multiply by two for your beats per minute (BPM). For accuracy, perform this in the morning before getting out of bed.
Using Technology for Precision
Modern technology offers convenient and precise ways to track your RHR:
- Fitness trackers and smartwatches continuously monitor your heart rate, providing comprehensive data.
- Smartphone apps use your phone’s camera to measure your pulse by detecting subtle color changes in your fingertip.
- Chest strap heart rate monitors offer highly accurate readings, especially during exercise.
Logging and Trend Analysis
Consistency is crucial when measuring RHR; maintain a daily log, noting conditions that may affect heart rate, such as stress levels, sleep quality, or recent exercise. Over time, this will help you identify patterns in how your RHR changes with lifestyle adjustments.
Conclusion
Proper lifestyle and habit changes can effectively reduce your resting heart rate. By incorporating regular aerobic workouts, stress management, a healthy diet, hydration, and quality sleep, you can significantly benefit your heart. The journey to improved cardiovascular fitness requires time and commitment, but a dedication to a healthier life can lead to a lower resting pulse rate for years to come.