Understanding Insomnia in Older Adults: Causes and Solutions
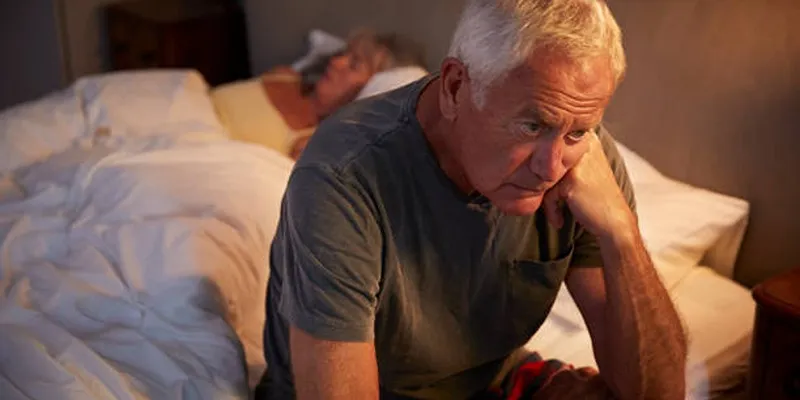
Insomnia is one of the leading sleep disorders affecting millions worldwide. It includes difficulties in initiating sleep, maintaining sleep, early waking, and the inability to return to sleep. While anyone can experience insomnia, older adults are particularly susceptible. Insomnia in the elderly is a significant concern as it impacts nearly every aspect of life.
Why Is Insomnia a Concern for Older Adults?
Sleep disorders in older adults can exacerbate existing health issues, impair concentration and memory, and increase the risk of falls or accidents. Often overlooked or considered normal, lack of sleep in the elderly needs addressing for a better quality of life.
Common Causes of Insomnia in Older Adults
 Several factors
can contribute to insomnia in older adults, including:
Several factors
can contribute to insomnia in older adults, including:
1. Physical Health Conditions
Chronic pain from arthritis, backaches, and musculoskeletal issues is a major cause of insomnia. Respiratory disorders like asthma and sleep apnea, as well as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease, can also affect sleep.
2. Mental Health Issues
Anxiety and depression are significant contributors to insomnia. Stress from finances, health, or feelings of isolation, prevalent in the elderly, can make it difficult to fall asleep.
3. Medication Side Effects
Medications for common conditions in older adults can disrupt sleep. For instance, beta-blockers for high blood pressure may cause nightmares, while diuretics can lead to frequent nighttime bathroom visits.
4. Changes in Sleep Patterns
As people age, they often become lighter sleepers and spend less time in restorative sleep stages. These changes mean older adults can wake up more easily due to noise or discomfort.
5. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
Lack of physical activity reduces the need for sleep. Factors such as shift work, evening screen use, noise, and temperature can also cause insomnia.
Effects of Insomnia on Older Adults
Insomnia extends beyond feeling tired; it has significant physical and mental health repercussions.
1. Daytime Fatigue
Poor sleep can leave older adults exhausted during the day, affecting their ability to stay active and engaged.
2. Cognitive Impairment
Chronic sleep deprivation can impair memory, focus, and decision-making, exacerbating age-related cognitive decline.
3. Increased Risk of Falls
Fatigue and reduced alertness can increase the likelihood of falls and accidents, particularly for those with mobility issues.
4. Mental Health Decline
Insomnia can lead to irritability and mood swings, worsening conditions like depression and anxiety, and significantly impacting quality of life.
Practical Tips to Manage Insomnia in Older Adults
 Managing
insomnia can be challenging, but several practical steps can help improve
sleep quality:
Managing
insomnia can be challenging, but several practical steps can help improve
sleep quality:
1. Establish a Soothing Bedtime Routine
A soothing bedtime routine signals your body to relax. Activities like reading, listening to soft music, or deep-breathing exercises can promote calmness and set the stage for a good night’s sleep.
2. Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate your internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally.
3. Optimize the Sleep Environment
Ensure the bedroom is conducive to sleep by keeping it quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature. A supportive mattress and blackout curtains can make a significant difference.
4. Stay Physically Active
Regular physical activity like walking, yoga, or tai chi can help older adults fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep. Avoid intense exercise close to bedtime.
5. Limit Stimulants and Heavy Meals
Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals before bedtime. If hungry at night, opt for a light snack like a banana or a glass of warm milk.
6. Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Techniques such as meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help calm the mind and prepare the body for restful sleep.
Long-Term Strategies for Better Sleep
Achieving restful and rejuvenating sleep is vital for overall health and well- being. Incorporate these long-term strategies into your daily routine for improved sleep quality.
1. Adopt Healthy Sleep Hygiene
Good sleep hygiene involves habits that promote high-quality sleep, such as limiting screen time before bed, avoiding long naps during the day, and creating a quiet, tech-free bedroom environment.
2. Address Underlying Health Issues
Treating conditions like chronic pain, sleep apnea, or restless leg syndrome can alleviate sleep problems. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for effective management.
3. Engage in Social and Cognitive Activities
Staying socially active and engaging in mentally stimulating activities, like puzzles or reading, can reduce loneliness and promote better sleep.
Conclusion
Insomnia is a common but manageable issue for older adults. Understanding its causes and adopting practical strategies can improve sleep quality and overall health. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene, maintaining an active lifestyle, and seeking medical advice when needed are key steps in overcoming insomnia.
Good sleep is crucial for aging well and maintaining a fulfilling, healthy life. If you or a loved one struggles with insomnia, start making small changes today to positively impact sleep and well-being.